Intro
The people that creates or uses crawlers to fetch information from a web page, know that you can lose access if the website owner add a WAF (Web Application Firewall) to the web page. This will certainly make your life more difficult.
Some examples of WAF are:
- CloudFlare WAF
- Imperva Cloud WAF
- AWS/Azure WAF
How it work?
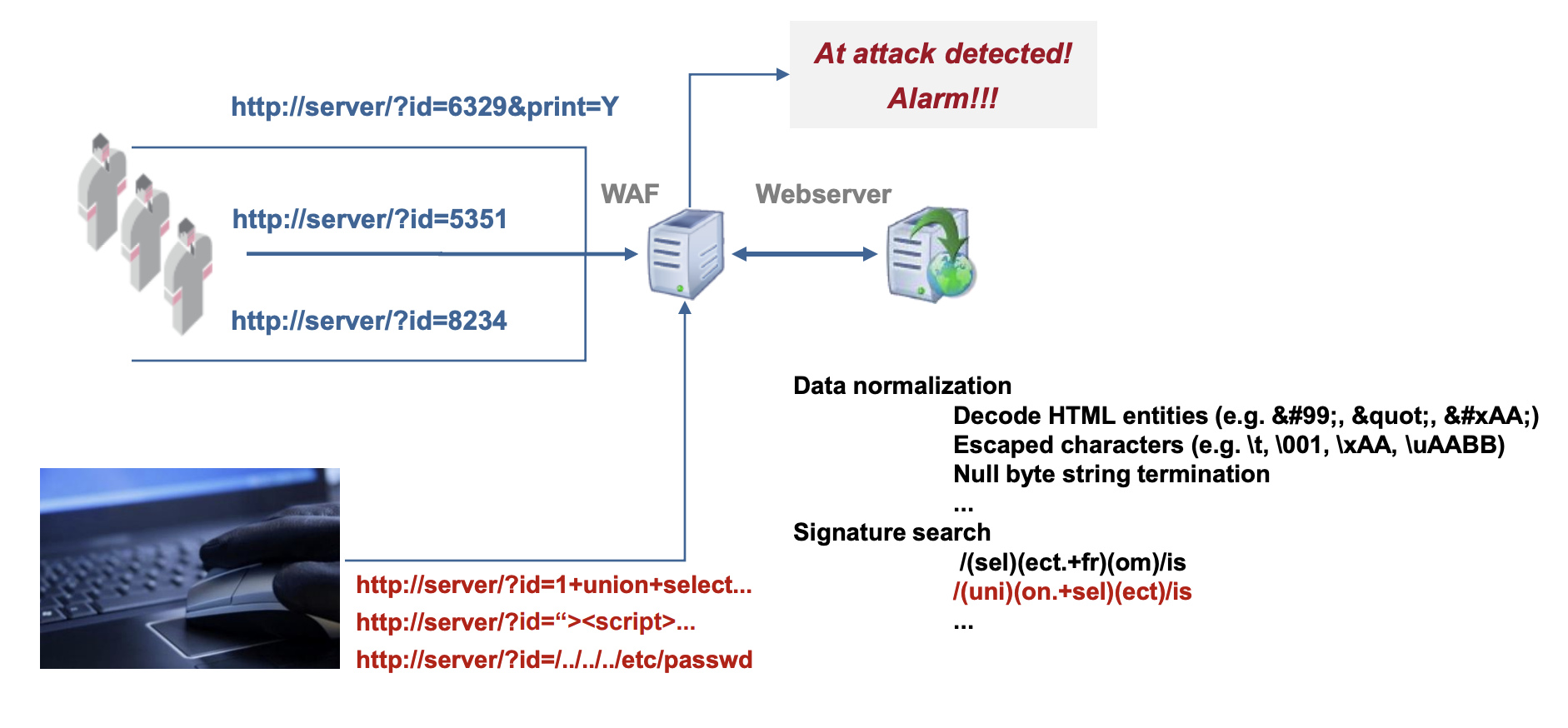
https://pt-corp.storage.yandexcloud.net/upload/corporate/ww-en/download/PT-devteev-CC-WAF-ENG.pdf
- Normally sits between the client and the server.
- Monitor and filters HTTP traffic between server and clients.
- Contains complex rules to detect malicious traffic.
- SQL Injections; XSS; TOR; Denial of Service (DoS), etc.
- Blocks malicious traffic.
Story
In one of my side projects I maintain some crawlers. Recently one stopped working after the website changed, but that wasn’t the only reason for the crawler to stop working, they also added a WAF to it.
My first reaction was to try to find a way to bypass it, so I’ve searched for a bit but I didn’t find anything relevant.
Normally there are some options to bypass a WAF depending on what you’re doing:
- HTTP Parameter Pollution
- HTTP Parameter Fragmentation
- nullbyte replacement
Since the URL wasn’t the same, I though maybe there was a way to access to the previous website? And maybe that isn’t protected by a WAF? The first thing that come to mind was to find the “origin” IP Address.
So the question was, is there a service that kept a record of different IP? Yes there is!
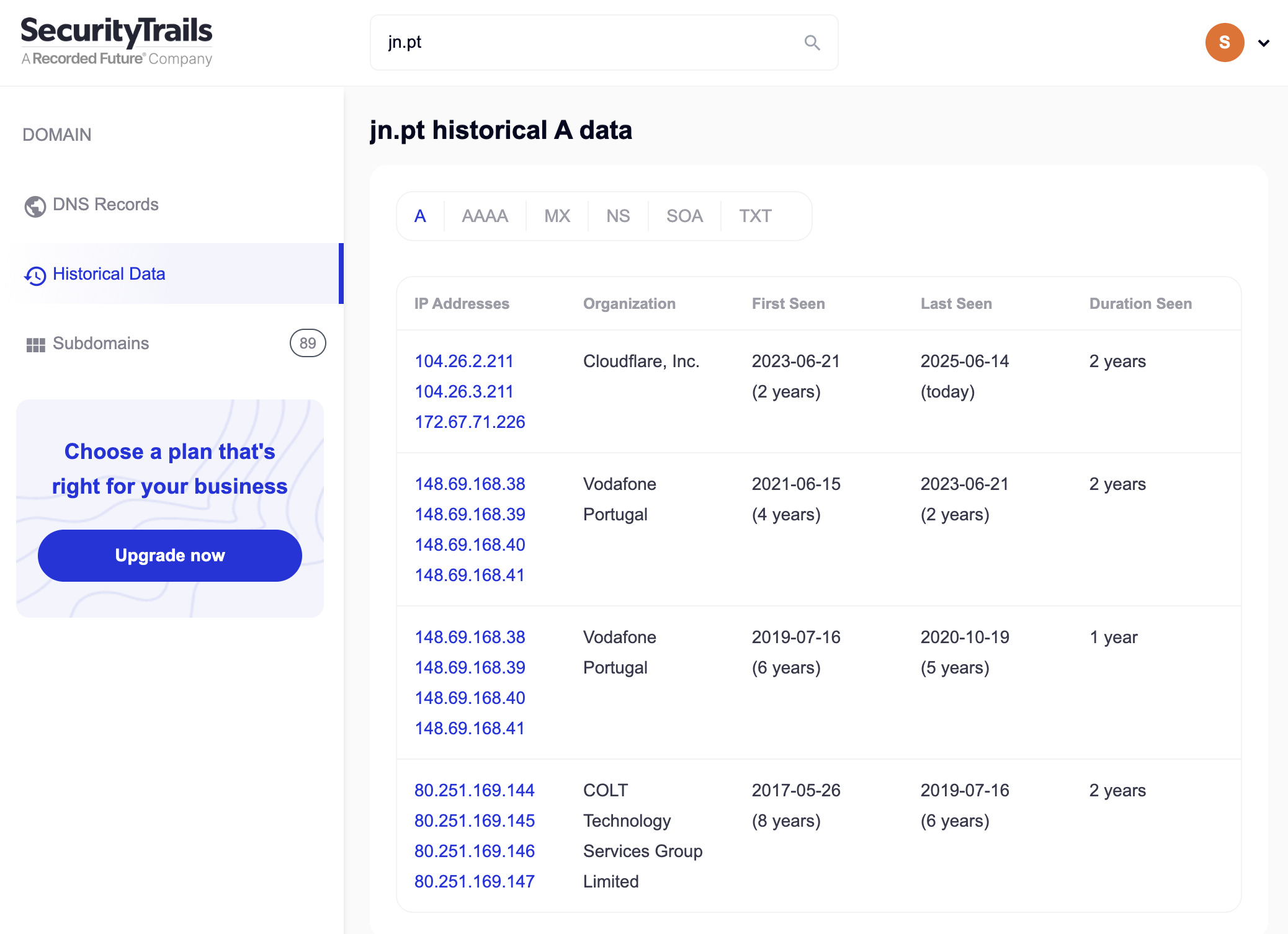
I’ve found Security Trails, a website that allow us to see historical data of a domain. My idea was if I can access directly to the IP address, maybe I could bypass the WAF, of maybe they still kept the old server running without the WAF.
With the old IP address, I confirmed that the old service is still working and being updated, so I updated the configuration on crawler to use the IP address instead of the domain, but added the domain under Host header so the server could redirect to the right host.
curl --header 'Host: jn.pt' http://148.69.168.38/
Now, the request that was being intercepted when requesting via TOR is able to request as previously.
We must be aware that since this is a deprecated service, it can be removed anytime and we need to fallback to the new service (and find a way to use it for this purpose).
Conclusion
How this can happen? Mostly on companies that aren’t tech aren’t their core, they forget to shutdown the old services or will take some time to decommission it.